Portuguese World Exhibition (Exposição do Mundo Português) 1940
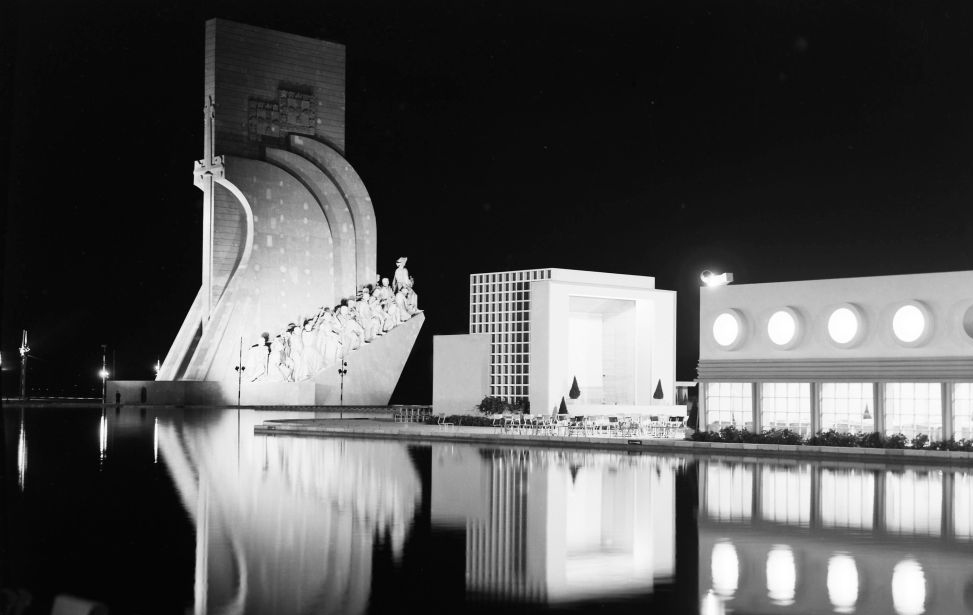

Along with a new marina, the 52 metres tall Monument to the Discoveries (Padrão dos Descobrimentos) was built overlooking the Tagus (Tejo) river to pay tribute to Portugal's heroes of its age of discovery. It was designed by Cottinelli Telmo in collaboration with Leopoldo de Almeida. Moored alongside the monument was a full-sized replica of a Portuguese galleon. The monument was dismantled after the fair but a permanent version of the piece was commissioned eighteen years later in 1958 to commemorate the 500 year anniversary of Infante Henry the Navigator's death.
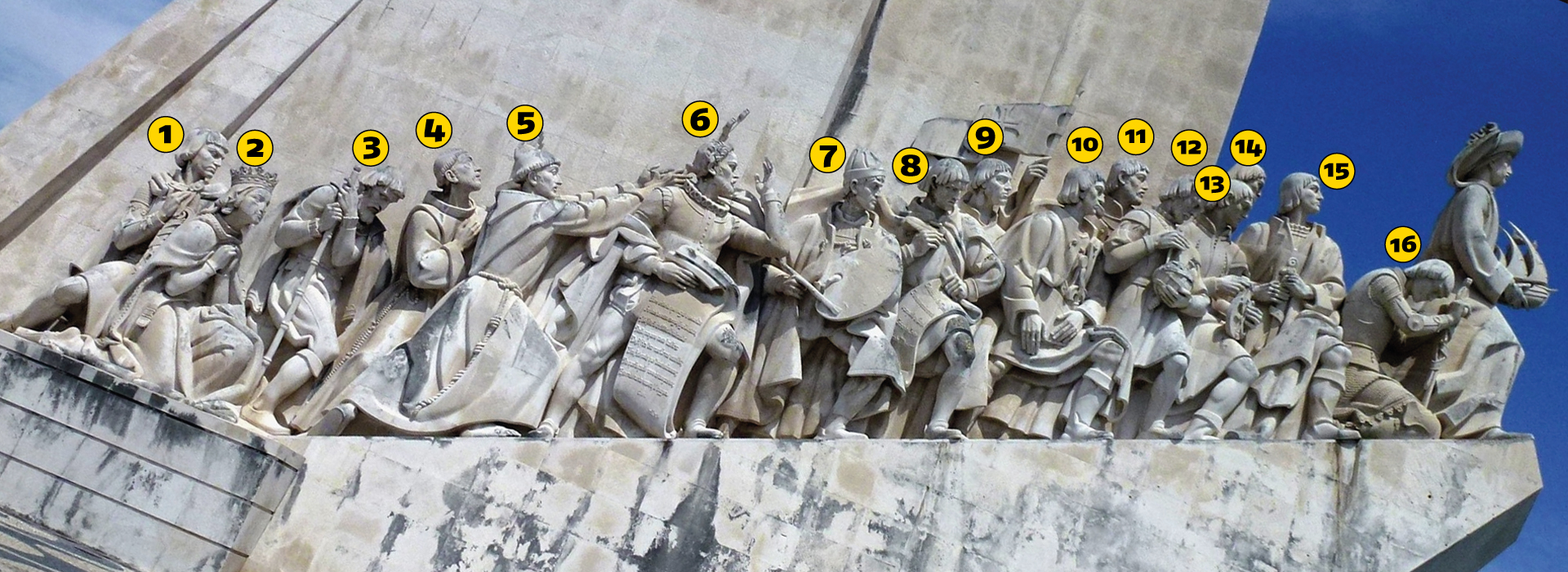
East Side Sculptures
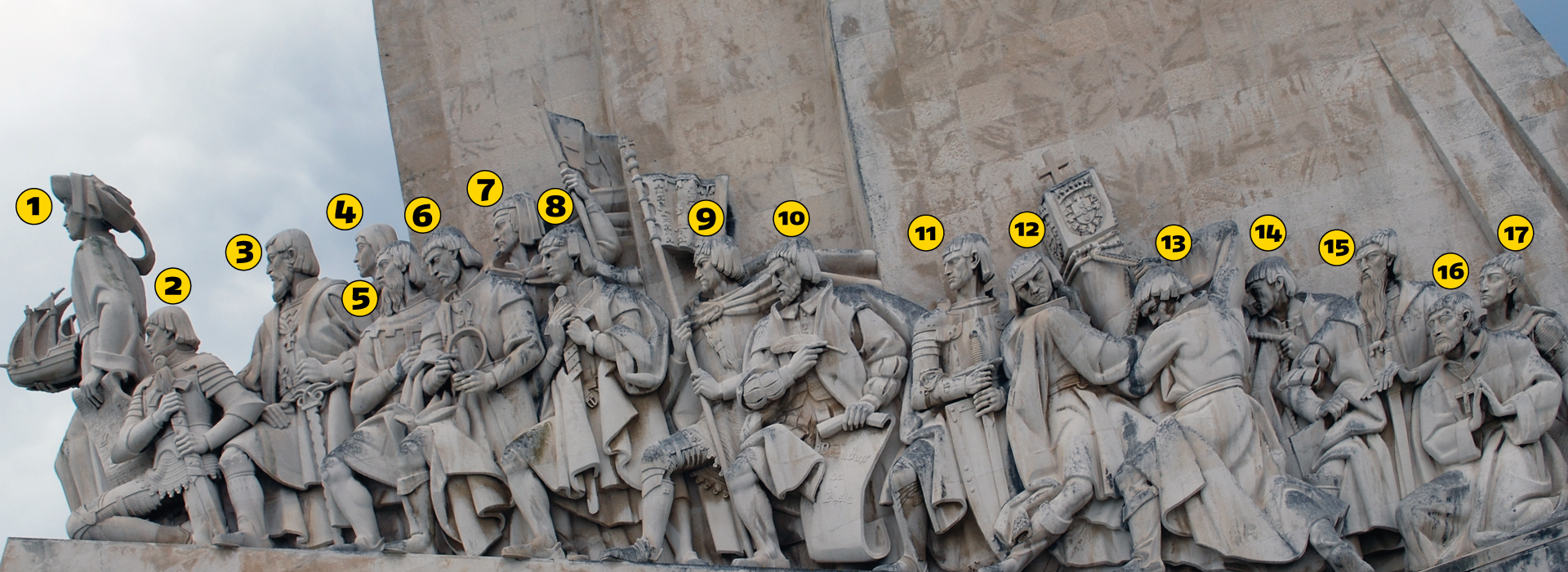

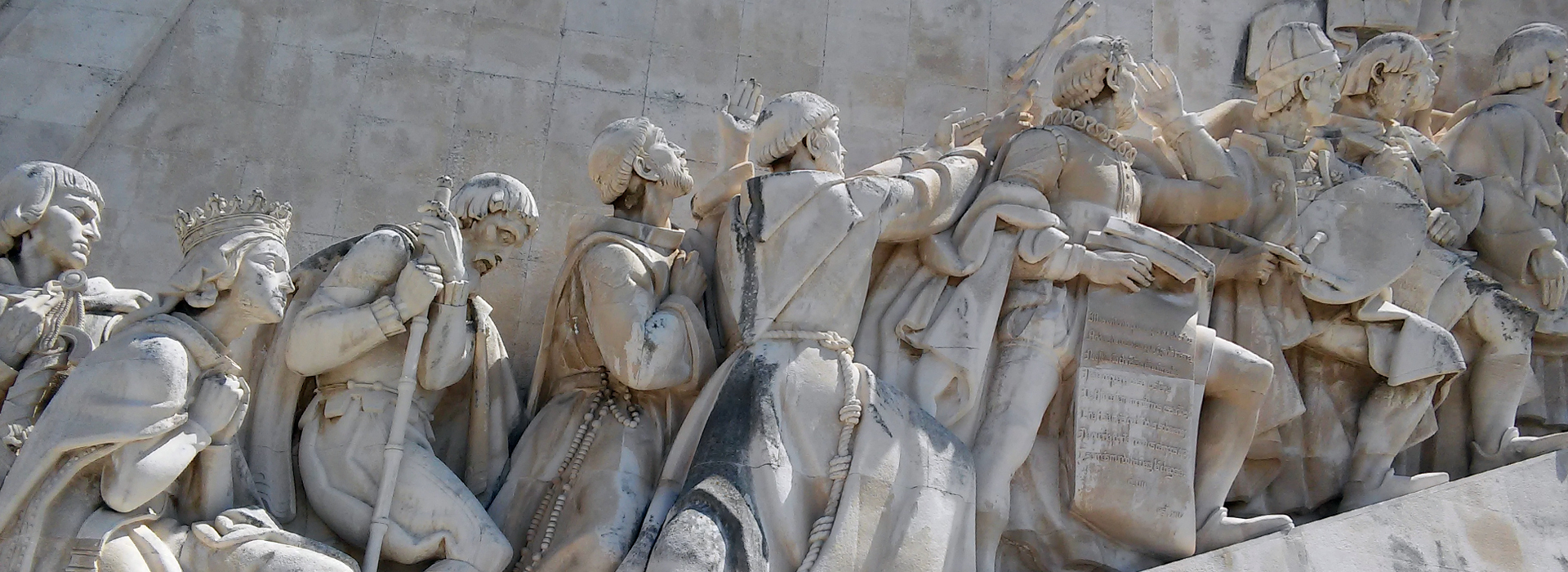
1. Henry the Navigator
Infante D. Henrique of Portugal, Duke of Viseu, better known as Prince Henry the Navigator was an important figure in 15th-century Portuguese politics and is regarded as the main initiator of what would be known as the Age of Discoveries. His statue standing at the helm of the monument he is depicted holding a model of a carrack.
2. King Afonso V
Afonso V was called the African (o Africano), who was from 1471 the first king of Portugal to claim dominion over a plural "Kingdom of the Algarves," instead of the singular "Kingdom of the Algarve." which now included territories gained in North Africa.
3. Vasco da Gama
The infamous portuguese explorer who was the first European to reach India by sea. His initial voyage to India (1497–1499) was the first to link Europe and Asia by an ocean route, connecting the Atlantic and the Indian oceans and therefore, the West and the Orient.
4. Afonso Baldaia
Afonso Gonçalves Baldaia explored much of the coast of Western Sahara in 1435–1436 on behalf of the Portuguese prince Henry the Navigator. He would later become one of the first colonists of Terceira Island in the Azores.
5. Pedro Álvares Cabral
A nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer who is regarded as the discoverer of Brazil. Cabral conducted the first substantial exploration of the northeast coast of South America and claimed it for Portugal.
6. Fernão de Megalhães
The explorer who organised the Spanish expedition to the East Indies from 1519 to 1522, resulting in the first circumnavigation of the Earth, completed by Juan Sebastián Elcano.
7. Nicolau Coelho
A navigator and explorer who participated in the discovery of the route to India by Vasco da Gama where he commanded Berrio, the first caravel to return. He was also the captain of a ship in the fleet headed by Pedro Álvares Cabral who landed in Brazil.
8. Gasper Côrte-Real
Along with his father João Vaz Corte-Real and brother Miguel, participated in various exploratory voyages sponsored jointly by the Portuguese and Danish Crowns. These voyages are said to have been some of the first to reach Newfoundland and possibly other parts of northeastern Canada.
9. Martim Afonso de Sousa
Born in Vila Viçosa, he was commander of the first official Portuguese expedition into the heart of the colony of Brazil.
10. João de Barros
Known as the Portuguese Livy João de Barros is one of the first great Portuguese historians, most famous for his Décadas da Ásia ("Decades of Asia"), a history of the Portuguese in India, Asia, and southeast Africa.
11. Estévão da Gama
Governor of Portuguese Gold Coast and Portuguese India, he was the son of Vasco da Gama. He campaigned agains the Ottoman in the Red Sea and in Ethiopia.
12. Bartolomeu Dias
A nobleman of the Portuguese royal household he was the first European to sail around the southernmost tip of Africa in 1488 thus reaching the Indian Ocean.
13. Diogo Cão
Also known as Diego Cam was an explorer and one of the most notable navigators of the Age of Discovery. He made two voyages sailing along the west coast of Africa in the 1480s, exploring the Congo River and the coasts of the present-day Angola and Namibia.
14. Antonio de Ábreu
In November 1511 with three ships, in an exploratory voyage to the 'Spice Islands' of Maluku, he led the first European expedition to reach Timor and the Banda Islands, in Indonesia, in 1512.
15. Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso advanced the three-fold Portuguese grand scheme of combating Islam, spreading Christianity, and securing the trade of spices by establishing a Portuguese Asian empire.[5] Among his achievements, Afonso was the first European of his Renaissance to raid the Persian Gulf, and he led the first voyage by a European fleet into the Red Sea.
16. St. Francis Xavier
St. Francis Xavier led an extensive mission into Asia, mainly within the Portuguese Empire of the time and was influential in evangelisation work, most notably in India.
17. Cristovão da Gama
The son of Vasco da Gama he was the military commander who led a Portuguese army of 400 musketeers on a crusade in Ethiopia and Somalia (1541–1543) against a far larger Adal Muslim army of Imam Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi aided by the Ottoman Empire. Along with the allied Ethiopian army he was victorious against greater odds in four battles. The last of which he was seriously wounded, after which he was captured and consequently executed.
TOP LISBON TOURS
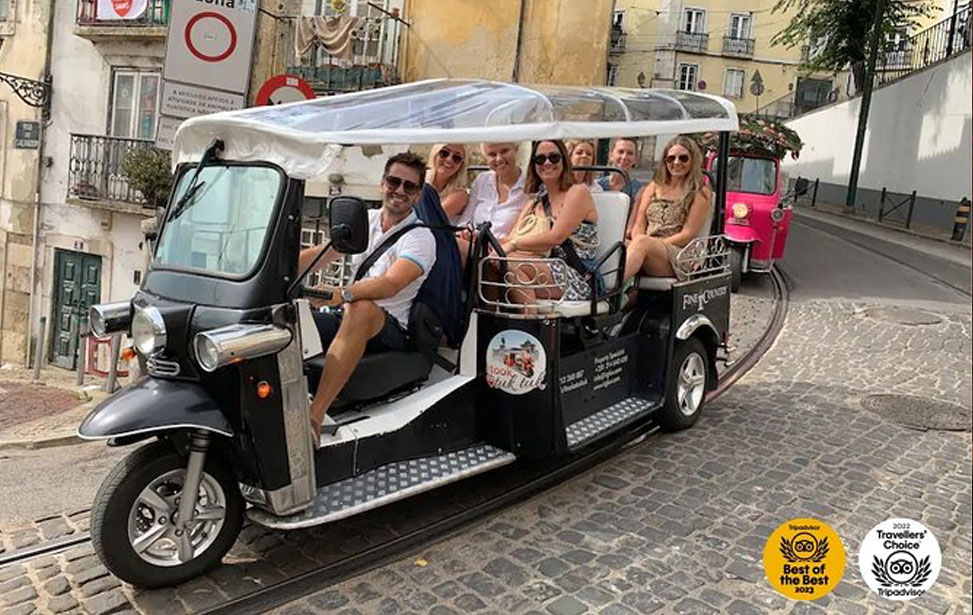

True 4 Hour TukTuk Tour of Lisbon
Experience Lisbon efficiently with a private half-day tuk-tuk tour, perfect for those seeking an eco-friendly way to explore the city. Personalise your itinerary and discover top attractions such as the historic Bairro Alto neighbourhood, the stunning Jerónimos Monastery and the breathtaking Miradouro da Senhora do Monte. Travel beyond the city centre to uncover multiple neighbourhoods while covering more ground quickly. This private tour offers flexibility and an intimate experience, allowing you to soak in Lisbon's vibrant atmosphere and iconic landmarks while enjoying the comfort of your private tuk-tuk.
(4,314) | 4 Hr | ✔ Free Cancellation
Check Availability
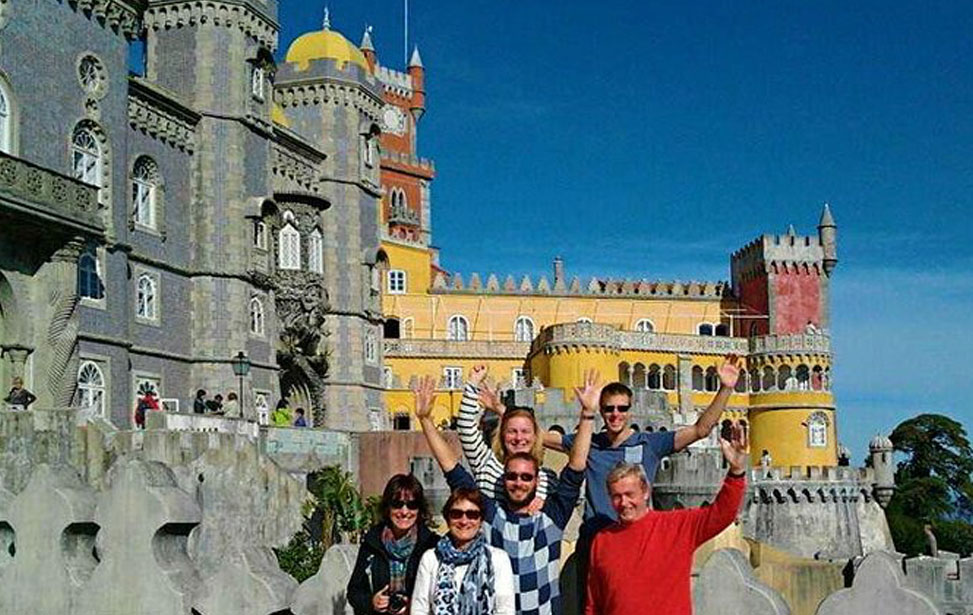

Full-Day Tour Best of Sintra and Cascais from Lisbon
Discover the enchanting beauty of Sintra on a full-day small-group tour from Lisbon. Explore the region's UNESCO-listed sites, including the majestic Pena Palace and charming Sintra Village. Witness stunning views from Cabo da Roca, Europe's westernmost point, and take in the coastal allure of the picturesque fishing village of Cascais. Enjoy personalised attention from your guide throughout this intimate experience, limited to eight people. Round-trip transportation from your Lisbon hotel is included, ensuring a seamless journey. Experience the romantic landscape of Sintra and Cascais on this unforgettable tour.
(753) | 8 Hr | ✔ Free Cancellation
Check Availability
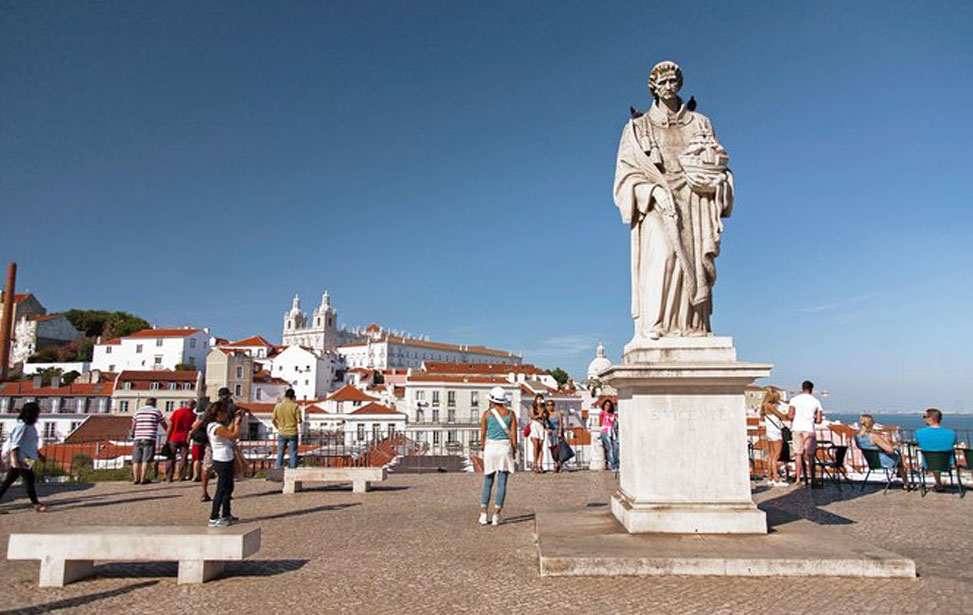

Private City Tour: Highlights of Lisbon
Explore the best of Lisbon on this private tour with an experienced guide. Journey through Portugal's capital, learning about its rich history while visiting top landmarks. Travel efficiently in an air-conditioned vehicle and discover historic districts like Chiado, Alfama, Baixa, and Belem on foot. Choose a morning or afternoon departure and enjoy convenient pickup and drop-off at your Lisbon hotel or cruise terminal. Taste the world-renowned pastel de Belém and immerse yourself in the charm of Lisbon. A private guide and vehicle provide a personalised experience as you uncover the highlights of the city.
(616) | 4 Hr | ✔ Free Cancellation
Check Availability
West Side Sculptures

1. D. Pedro, Duke of Coimbra
He was a prince of the House of Aviz, son of King John I of Portugal and his wife Philippa of Lancaster, better known in Portugal as Infante D. Pedro das Sete Partidas [do Mundo], "of the Seven Parts [of the World]" because of his extensive travels.
2. Queen Philippa of Lancaster
Philippa of Lancaster, or Filipa de Lencastre, was the English born Queen of Portugal the wife of King João I. Their union secured the Treaty of Windsor and produced several children who became known as the "Illustrious Generation" in Portugal.
3. Fernão Mendes Pinto
This charismatic explorer and writer recorded his Pilgrimage voyages in his autobiographical memoir. The historical accuracy of some of his work is questionable and somewhat far fetched which earned him the nickname "Fernão Mentes Minto" (wordplay of the Portuguese verb mentir 'to lie').
4. Frei Gonçalo de Carvalho
A missionary who belonged to the Order of the Dominicans and spread the gospel to India and created Catholic communities.
5. Henrique Soares de Coimbra
A Franciscan Missionary who worked in Brazil and East Asia.
6. Luís de Camões
Luís Vaz de Camões is widely considered be Portugal's and the Portuguese language's greatest poet and is often compared to Shakespeare, Vondel, Homer, Virgil and Dante. He wrote a considerable amount of lyrical poetry and drama however his most revered work is his epic work Os Lusíadas (The Lusiads). The influence of this masterpiece is so profound that Portuguese is often refered to as the "language of Camões".
7. Nuno Gonçalves
Nuno Gonçalves was the 15th-century Portuguese court painter for King Afonso V who is credited for the painting of the Saint Vincent Panels (Paineis de São Vicente de Fora). The panels depict the main elements of Portuguese society in the 15th century: clergy, nobility and common people. The panels are now housed in the Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga (National Museum of Ancient Art).
8. Gomes Eanes de Zurara
Gomes Eanes de Zurara was a Portuguese chronicler of the Age of Discovery, the most notable after Fernão Lopes.
9. Pêro da Covilhã
Born in Covilhã, Pedro was a Portuguese diplomat and explorer. He first worked for Castile, in the service of Don Juan de Guzmán, before returning to Portugal and attached himself, first as a groom, then as a squire, to Afonso V of Portugal and his successor John II of Portugal. He is best known for his explorations in the Near East and the adjoining regions of Asia and Africa.
10. Jácome de Maiorca
From Jewish descent Jacomo de Mallorca was a leading cartographer in the employ of Henry the Navigator, skilfully adding newly attained territories, discoveries and trade routes to an ever-increasing global map. His techniques were later passed on at the Navigators School in Sagres.
11. Pêro Escobar
Pêro or Pedro was the navigator who discovered São Tomé in 1471, Annobon, Príncipe in 1472. He is then recorded sailing with Diogo Cão on his first voyage in 1482 and as the pilot of the famous Bérrio caravel on Vasco da Gama's first expedition in 1497 to sail directly from Europe to India. He was also on Pedro Álvares Cabral's discovery of Brazil in 1500.
12. Pedro Nunes
Nunes is considered to be one of the greatest mathematicians of the middle ages and is renown for his contributions in the nautical sciences. He was the first to apply mathematics to navigation and cartography. He was the first to propose the idea of a loxodrome and was the inventor of several measuring devices, including the nonius (from which Vernier scale was derived), named after his Latin surname.
13. Gil Eanes
Eanes was born in Lagos and joined the service of Prince Henry's expeditions in 1433. He was the first European to round the Cape Bojador of West Africa which opened the way for the subsequent Portuguese explorations of Africa.
14. Péro de Alenquer
Pêro accompanied Bartolomeu Dias on his journey around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487/1488. He was the pilot of Vasco da Gama's flagship on the latter's first voyage to India and later wrote his adventures.
15. João Gonçalves Zarco
João established settlements and recognition of the Madeira Islands, and was appointed first captain of Funchal by Henry the Navigator.
16. Ferdinand the Holy Prince
Often referred to as the "Saint Prince" or the "Constant Prince", Ferdinand was the youngest of the "Illustrious Generation" of 15th-century Portuguese princes of the House of Aviz and lay administrator of the Knightly Order of Aviz.
TOP BELÉM TOURS
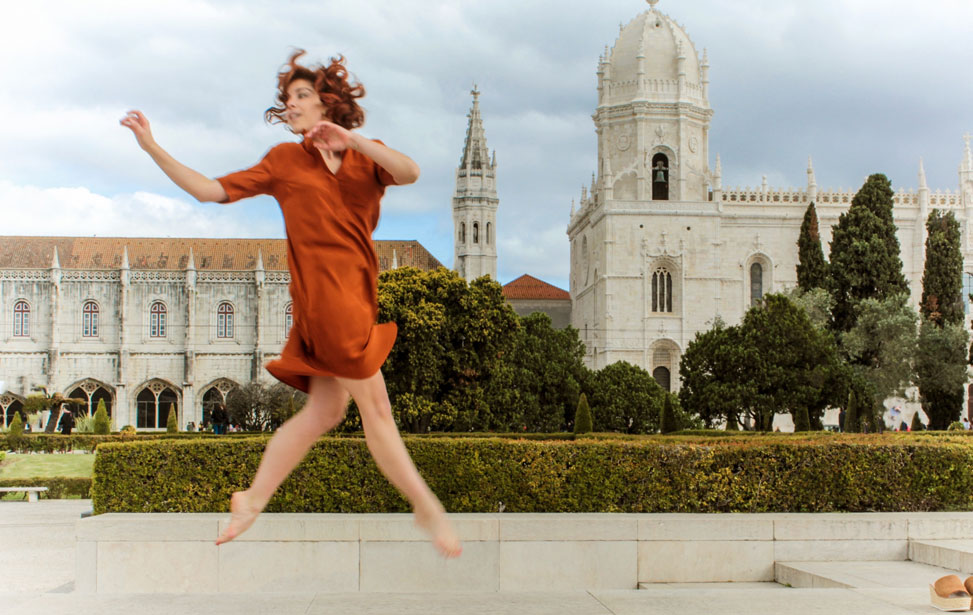

Belém Walking Tour and Jerónimos Monastery Ticket
Explore Lisbon's Age of Discoveries on this guided walking tour in Belém. Visit iconic sites like Belém Tower and enjoy skip-the-line access to the Jerónimos Monastery. Meet your guide in the Garden of Afonso de Albuquerque and travel back in time. Indulge in an authentic Pastéis de Belém and savour the famous egg tarts. Marvel at the late Gothic architecture of the UNESCO-listed Jerónimos Monastery.
Stroll along the river to the modern monument dedicated to Portuguese explorers. Enjoy breathtaking views where the Atlantic Ocean meets the Tagus River at Belém Tower. Create unforgettable memories and receive personalised recommendations for your Lisbon visit.
(233) | 5 Hr | ✔ Free Cancellation
Check Availability
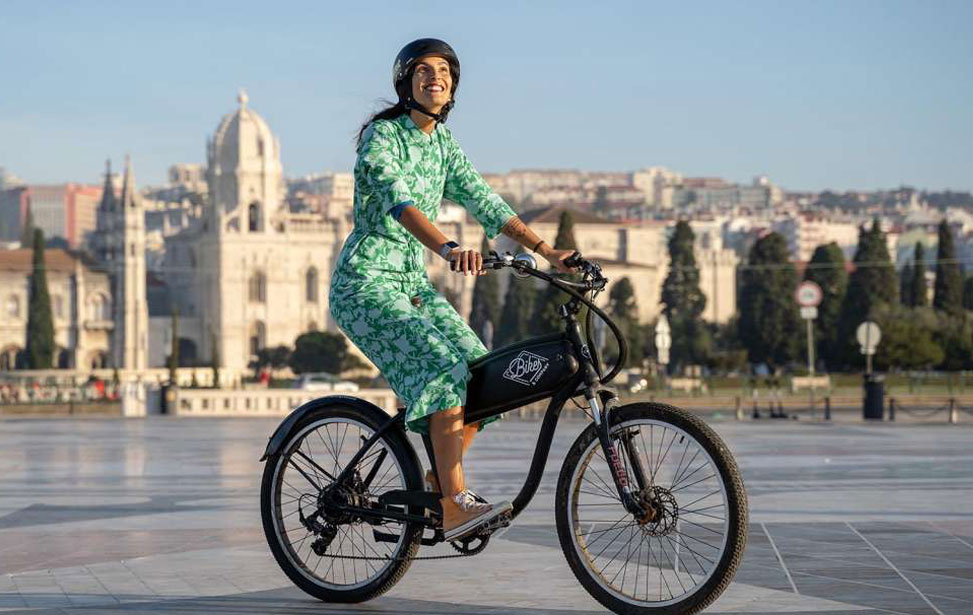

Electric Bike Tour by the River to Belém
Embark on a relaxing tour along Lisbon's riverside, starting in the cosmopolitan city centre. As you journey toward Belém, the vibrant energy of this European capital transitions into a more tranquil atmosphere. Travelling along the riverside provides an enjoyable journey filled with light, scenic landscapes, and lively city life. Belém offers history enthusiasts a glimpse into the Portuguese Discoveries, with its grand architecture and storied past. This neighbourhood was the launch point for many renowned explorers, shaping Portugal into the first global empire. This tour offers a harmonious blend of serenity and urban charm. Explore bustling riverfront esplanades, lush green fields, and talented local musicians, joggers, and artists capturing Lisbon's essence.
(388) | 3 Hr | ✔ Free Cancellation
Check Availability
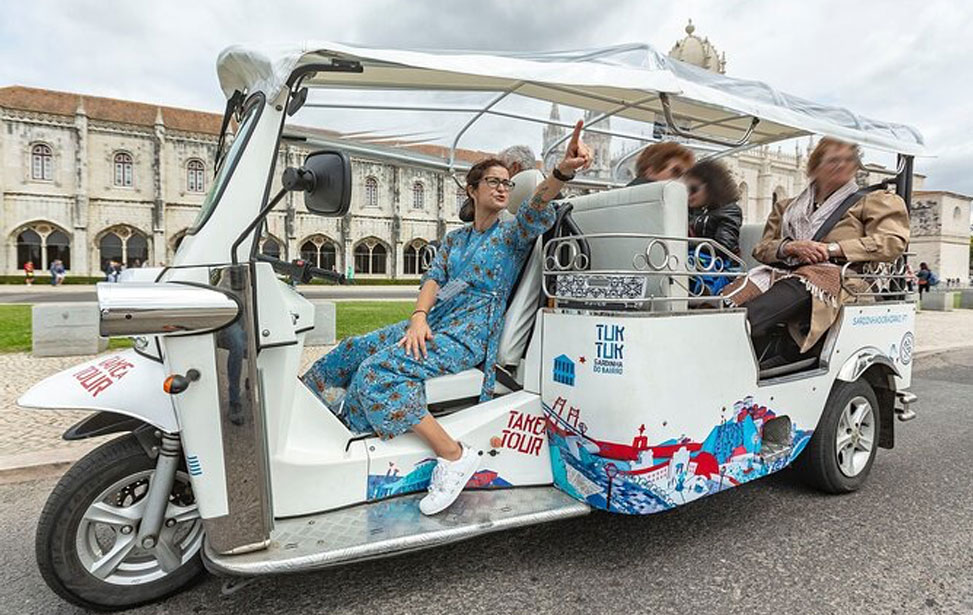

Discovering Belém Tuk Tuk Tour
Explore the historic Belém district of Lisbon with a two-hour tuk-tuk tour along the Tagus River. Admire the magnificent Jerónimos Monastery and its beautiful church, showcasing Portugal's architectural brilliance.
Visit the iconic Belém Tower, where Portuguese explorers embarked on their 1500 journey that led to the discovery of Brazil. Discover the Padrão dos Descobrimentos monument, paying tribute to key figures of Portugal's Age of Discoveries.
Before leaving Belém, savour the delectable Pastéis de Belém, the famous custard tarts that are known worldwide. This tour offers a perfect blend of history, culture, and culinary delights, making it a must-experience in Lisbon.
(37) | 2 Hr | ✔ Free Cancellation
Check Availability
Compass Rose (Rosa-dos-Ventos)
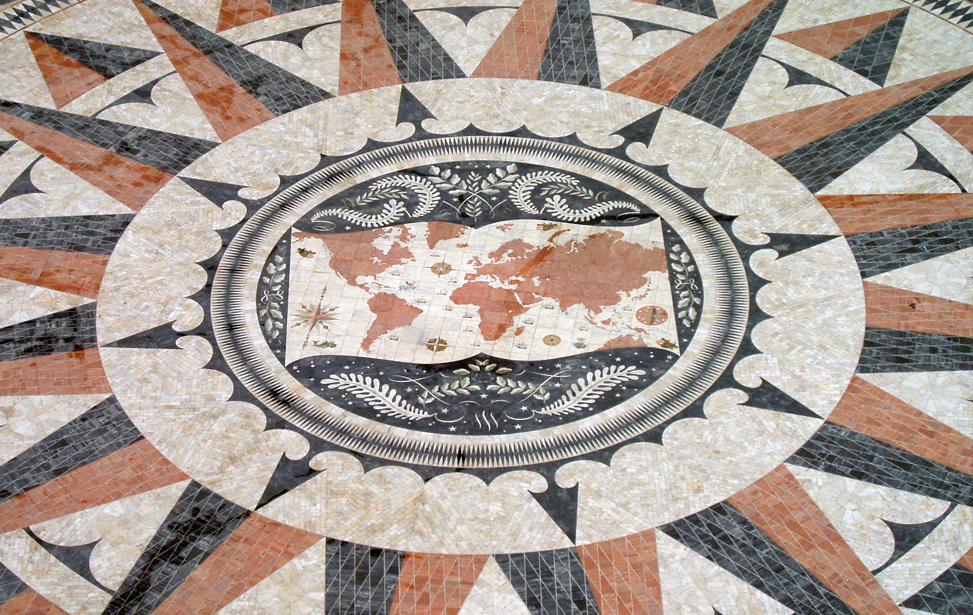

The best way to truly appreciate the Compass Rose is to head on inside the monument and take the lift that whisks visitors to the viewing gallery at the top. It has great views over the forecourt, Jerónimos Monastery and the Belém tower on one side and the river to the other.
October to April, Tuesday to Sunday: 10h00 - 18h00 | Monday: Closed
May to September, Tuesday to Sunday: 10h00 - 19h00 | Monday: Closed
Adult: €5.00, Family ticket: 2 adults + 2 children 12-18 yrs: €12.50, Concessionary: €2.50
Getting to the Monument to the Discoveries
| 714, 727, 729, 751 | |
| 15 | |
|
Linha Cascais trains stop at the Belém Train Station Timetable Trains of Portugal Website |
|
| Belem River Station: Hop On, Hop Off Boat |


 Lisbon Card Discounts
Lisbon Card Discounts